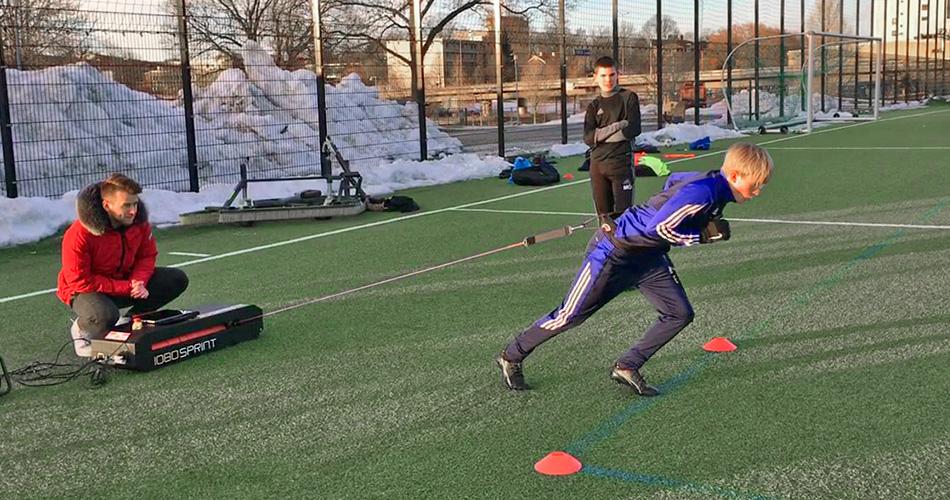
Title: unleashing Turf Potential: The Impact of Resisted Sprinting on Horizontal Strength
In the world of athletics, the quest for enhanced performance often leads coaches and athletes alike to explore innovative training methodologies. One such method gaining traction in recent years is resisted sprinting—a technique that combines sprinting with external resistance to amplify strength and speed. The Sport Journal delves into a compelling new study examining the effects of resisted sprinting on the production of horizontal strength, a crucial component for success in a variety of sports. as athletes push against added resistance, they not only unlock their sprinting potential but also may redefine the very dynamics of their strength training regimens.This article explores the findings, implications, and future directions of integrating resisted sprinting into athletic training, shedding light on how harnessing resistance could lead to breakthroughs in horizontal strength development and overall athletic performance.
Exploring the Mechanics of Resisted Sprinting and Its Impact on Horizontal Strength Development
Resisted sprinting is rapidly gaining recognition for its notable role in enhancing horizontal strength, a critical component for athletes involved in various sports. By incorporating external resistance—such as sleds, bands, or weighted vests—athletes can cultivate greater force production through improved muscle recruitment patterns. This method stimulates the neuromuscular system, leading to adaptations that can increase acceleration and top-end speed. The application of loading during sprints mirrors resistance training principles, allowing athletes to experience a greater overload, which, in turn, facilitates enhanced adaptation in muscle fiber composition and strength development. key benefits of resisted sprinting include:
- Improved acceleration: The added resistance forces athletes to exert more energy, enhancing their explosiveness.
- Increased power output: Engaging more muscle fibers leads to higher levels of power production.
- Enhanced metabolic conditioning: The rigorous demands of resisted sprinting can improve overall endurance levels.
Research indicates that the effects of resisted sprinting extend beyond immediate performance enhancements. Over time, regular engagement in this training modality leads to notable structural changes within the muscles involved. Analysis ofathletic performance illustrates that athletes utilizing resisted sprinting as part of their training regimen not only see increases in speed but also fortify their horizontal strength. A recent study exploring the correlation between resisted sprinting and strength gains presented compelling data:
| Training Method | Strength Gain (%) | Speed Advancement (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Sprinting | 8% | 0.5 m/s |
| Resisted sprinting | 15% | 1.2 m/s |
The data clearly illustrates that athletes who incorporate resisted sprinting experience superior strength gains and speed improvements compared to those who rely solely on conventional sprinting methods. Thus, as sports professionals increasingly explore innovative training techniques, it becomes evident that resisted sprinting is not just a fad but a scientifically-backed approach to developing essential athletic performance metrics.
key Findings on Performance Improvements Through Resisted Sprinting Techniques
Recent studies have highlighted the significant impact of resisted sprinting techniques on enhancing horizontal strength, which is a crucial component for athletic performance across various sports. Resisted sprinting, using methods such as sled pulls or harnesses, not only challenges an athlete’s explosive power but also stimulates muscle activation in a way that traditional sprinting cannot. Key benefits identified include:
- Increased force production during acceleration phases
- Improved sprinting technique through enhanced neuromuscular coordination
- Greater development of fast-twitch muscle fibers,leading to improved overall speed
additionally,performance metrics have shown promising results when athletes incorporate resisted sprinting into their training regimens. As an exmaple, a comparative study revealed that participants who engaged in resisted sprinting exhibited an average increase of 15% in their 30-metre sprint times compared to those who did not. The following table illustrates these findings:
| Training Method | Average Speed Increase |
|---|---|
| Traditional Sprinting | 5% |
| Resisted Sprinting | 15% |
Practical Recommendations for Athletes to Enhance Strength Training Regimens
Athletes looking to enhance their strength training regimens can implement a series of practical strategies to maximize their results on and off the field. Engaging in resisted sprinting is one effective method, as it not only builds horizontal strength but also translates into improved speed and acceleration. To effectively integrate this training technique, athletes should consider the following recommendations:
- Incorporate Variable Resistance: Utilize resistance bands or sleds during sprinting sessions to create varying levels of resistance, tailoring workouts to specific strength needs.
- focus on Sprint Mechanics: Ensure proper form and techniques are maintained throughout resisted sprints to prevent injury and enhance performance gains.
- Schedule Recovery Days: Allow for adequate recovery between high-intensity resistive workouts to prevent overtraining and promote optimal strength gains.
- Assess Progress Regularly: Monitor sprint times and strength metrics to identify improvements and adjust training protocols as necessary.
Furthermore, integrating resistance training exercises into the athlete’s routine can considerably support sprinting performance. Below is a simple table showcasing recommended exercises along with their primary benefits:
| Exercise | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Squats | Builds overall leg strength |
| Deadlifts | Enhances hip and core strength |
| Lunges | Improves balance and unilateral strength |
| Power Cleans | Boosts explosive strength and power |
Insights and Conclusions
the research presented in “The effect of Resisted Sprinting on the Production of Horizontal Strength” underscores a pivotal advancement in our understanding of athletic training methodologies. As athletes and coaches increasingly seek innovative ways to enhance performance, the findings suggest that incorporating resisted sprinting can significantly bolster horizontal strength, a key component in numerous sports. The implications of this study are far-reaching, offering a potential paradigm shift in training regimens across various disciplines. As further research builds upon these initial insights, it will be crucial for practitioners to stay informed and adapt their techniques accordingly, ultimately striving for improved athlete performance and competitive edge. the Sport Journal will continue to monitor developments in this area, ensuring readers remain at the forefront of sports science and training innovations.