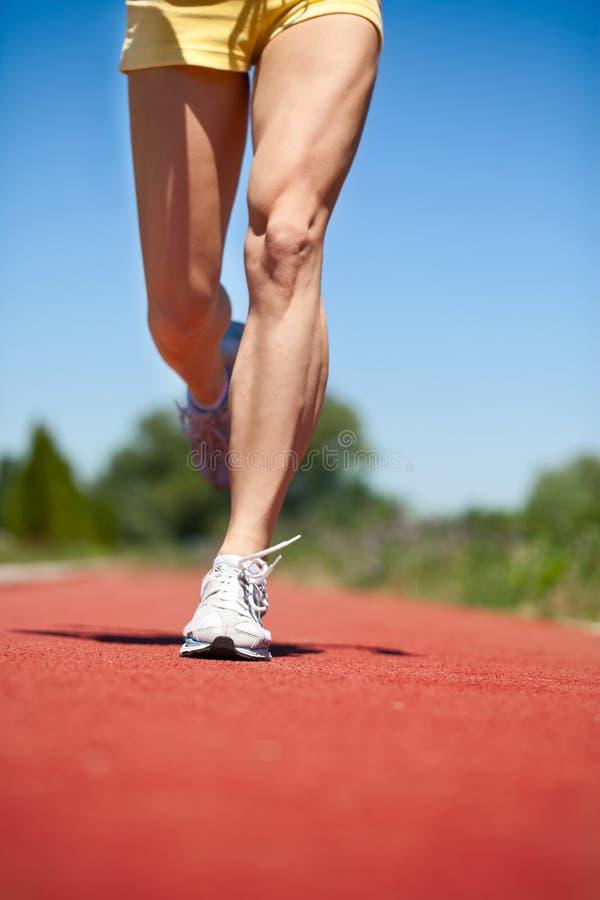
In the world of competitive athletics, sprinters are often celebrated for‚ĀĘ their explosive speed and agility, qualities that set them apart on the track. Recent research highlighted by EurekAlert!‚Ā£ sheds light on a captivating ‚Äćparadox: the ‚Ā§powerful muscular structure‚Äč of sprinters’ legs does ‚Ā£not impede their maneuverability. This revelation challenges long-held assumptions about muscle mass and mobility,suggesting that the secret to a sprinter’s success lies not only in sheer strength but also in the intricate balance between muscle development and versatility. As ‚ĀĘathletes ‚Äćstrive‚ĀĘ to shave precious seconds off their times, understanding the mechanics of their ‚Ā§lower limbs could hold the key to unlocking new‚Ā£ levels of performance.‚ĀĘ In‚Ā£ this article, we delve into the ‚Äčscience behind sprinter’s legs, exploring the unique‚ĀĘ adaptations‚Ā£ that allow thes elite athletes to dominate the ‚ÄĆtrack without sacrificing agility.
The Dual Role ‚ĀĘof Sprinter Legs: Power and Agility in High-Performance Athletics
Sprinters are often celebrated ‚Äćfor their ‚ĀĘexplosive speed,‚Ā£ a trait that is largely‚Äć attributed to‚Ā§ the unique ‚Ā§muscular ‚Äćcomposition of their ‚ÄĆlegs. These‚Ā£ athletes combine power with agility, resulting in a lower body that is not only ‚Ā£strong but also exceptionally‚Ā£ flexible.‚ĀĘ The muscles in a‚Äć sprinter’s legs, notably the quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, and gluteals, undergo rigorous training that‚Äč enhances both their size and functionality. This dual focus allows sprinters‚ĀĘ to achieve remarkable ‚Äčacceleration‚Ā§ from a standing start,‚Äč while‚ÄĆ also providing the necessary flexibility to navigate tighter turns and maintain ‚ÄĆbalance‚Äč throughout their‚Ā£ runs.
Key components‚Ā§ contributing to this remarkable adaptability include:
- Fast-twitch muscle ‚Äčfibers: These fibers ‚Äćare essential for rapid, forceful movements, allowing‚ÄĆ sprinters to propel themselves forward at ‚Ā£astonishing speeds.
- Joint ‚Ā£mobility: A sprinter’s ability to move their legs effectively through a full range ‚Äčof motion helps reduce injury risk and improve performance.
- Strength training: Targeted weightlifting not only builds ‚ÄĆmuscle but also enhances coordination and control, vital ‚Ā£for‚Ā§ maintaining speed and‚Ā£ agility‚ĀĘ during ‚ĀĘcompetition.
The interplay between strength ‚Ā§and dexterity ultimately defines a sprinter’s ability to excel. As research‚Ā£ indicates, the most triumphant athletes frequently enough exhibit a balance ‚Äčbetween explosive power and ‚Ā§nuanced movement techniques, enabling them to adapt quickly in dynamic race conditions. This intricate balance can be summarized in the‚Ā§ table below, emphasizing the relationship between muscle type, training focus, and performance outcome among elite sprinters:
| Muscle Type | Primary‚Ā£ Role | Training‚Äć Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Fast-twitch | Power ‚Äćgeneration | High-intensity interval‚ĀĘ training |
| Slow-twitch | Endurance | Steady-state cardio sessions |
| Mixed fibers | Agility ‚ÄĆand balance | Plyometric exercises |
Understanding Muscle Composition and Adaptation in elite Sprinters
Elite sprinters exhibit a unique blend of muscle composition‚ĀĘ that maximizes both ‚Äčpower ‚ĀĘand agility, enabling them‚Äć to ‚Äčperform at peak levels during ‚ĀĘcompetition. Their muscular build primarily consists of‚Ā§ fast-twitch muscle fibers, ‚Äćwhich are ‚Äćresponsible for ‚ÄĆrapid bursts ‚Ā§of speed and explosive strength.This adaptation allows sprinters ‚Äćto generate high levels of‚Äč force quickly, ‚Äćessential for propelling‚ÄĆ themselves‚ÄĆ down the track. The ‚ĀĘsignificant proportion of these fibers‚Äć provides advantages ‚Äćin maximal sprinting and acceleration, ‚ĀĘwhile also ensuring that the athletes maintain a level ‚ÄĆof maneuverability that is‚ĀĘ critical during races. Key‚Ā§ attributes of their ‚Äćmuscle composition include:
- Hypertrophy: Increased muscle size contributes to greater contractile force.
- Muscle Plasticity: Rapid ‚Ā£adaptation to varying training stimuli ‚Ā£enhances performance.
- Efficient Energy Utilization: ‚ĀĘ Enhanced‚Äć metabolic ‚Ā§pathways support explosive ‚Ā§movements.
Sprinting training ‚ÄĆnot only focuses on ‚ÄĆbuilding strength but also on enhancing the coordination‚Äć and‚Äć efficiency of muscle contractions. The combination‚ÄĆ of types I‚Äć and II muscle fibers results in a unique‚Ā£ muscle profile that enables sprinters to react‚ÄĆ quickly while retaining optimal ‚Äćbody control. Research shows that elite athletes ‚Äćfine-tune their muscle ‚Äćdevelopment through a variety of training techniques, emphasizing not ‚ĀĘjust ‚Äčthe size and strength of their muscles, but also the proficiency with which those muscles work‚Äć in harmony. The following table summarizes ‚Ā§essential training elements and ‚ÄĆtheir ‚Ā§effects on muscle adaptation in sprinters:
| Training Element | Effect on Muscle Composition |
|---|---|
| Strength Training | Increases muscle mass and explosive‚Ā§ power |
| Plyometrics | enhances muscle elasticity and reactive strength |
| Speed Drills | Improves neuromuscular coordination and quickness |
Training Techniques to Enhance Speed and Flexibility in Sprinting Performance
In the pursuit of optimizing sprinting‚Äć performance, athletes are increasingly turning to specialized ‚ĀĘtraining techniques that focus on‚Äč enhancing both speed and flexibility. Sprinting demands not only explosive power but also the ability to execute ‚ÄĆrapid‚Äč movements efficiently. To achieve this, athletes‚ĀĘ can incorporate dynamic ‚Äćstretching routines and plyometric exercises into‚Äč their training regimens.Dynamic stretches, which involve controlled ‚ĀĘleg and arm swings, facilitate ‚Äčgreater range of motion ‚Äćand prepare‚Ā£ the muscles‚Äč for intense exertion. ‚ĀĘPlyometrics, such as ‚Ā£box jumps and bounding, develop muscular power and explosiveness, crucial for improving acceleration during ‚Äčsprints.
In conjunction with‚ÄĆ these techniques, incorporating strength training that ‚Äćemphasizes agility ‚ĀĘand core stability plays ‚Äća vital role in supporting overall performance. Exercises such as the single-leg deadlift and lateral lunges ‚Ā£ specifically‚Äć target essential muscle groups that contribute to sprinting mechanics while‚Äč enhancing flexibility.‚ĀĘ Furthermore, interval training, which ‚ÄĆalternates short bursts of intensive sprints with recovery phases, is ‚ÄĆproven ‚Ā§to increase both speed‚ĀĘ and endurance. The strategic combination of these training‚ĀĘ components not only promotes muscular development but also ensures that sprinters maintain the fluidity and agility required for optimal performance on the track.
Insights and Conclusions
the remarkable anatomy‚ÄĆ of sprinters’ legs underscores the ‚Ā£delicate‚Äć balance between muscle mass and agility ‚ÄĆthat defines elite‚ĀĘ athletic performance.As recent‚Ā£ findings highlighted in EurekAlert! illustrate,the highly‚Ā§ muscular‚Ā§ structure‚Äć of sprinters’ legs is not merely an aesthetic ‚Ā§advantage but a critical‚Äč component ‚ĀĘof their ‚ÄĆability to maneuver rapidly‚ĀĘ and efficiently on the track. The interplay of strength and flexibility emerges as ‚ĀĘa‚Ā§ key factor in their success, paving‚Äč the way for future research ‚Ā£into‚ĀĘ optimizing athletic training and performance. As we gain deeper insights into the mechanics behind ‚Äćthese athletes, it‚Ā§ becomes increasingly clear that the‚Ā§ legs of‚ĀĘ sprinters represent not just ‚ĀĘpower, but an elegant fusion of form and function that‚Äć continues to‚Ā£ inspire both ‚Äčscientific exploration and admiration ‚ÄĆin the realm of sports.